Storage in AWS
Storage in AWS
There are 3 major storage type in AWS :
- Block storage (Elastic Block Storage - EBS)
- File storage (Elastic File Storage - EFS)
- Object storage (S3 bucket)
HDD and SSD are the main storage units for all these three.
Block storage - HDD and SSD are the devices that uses blocks to store information inside. Blocks are small fragment/cluster of data. Basically AWS provides this so that we can partition and format it easily. They are ideal for applications that require low-latency access to data, such as databases and enterprise applications.
File Storage - Is different than block storage, while under the hood it depends on block based storage units, it is connected to internet so that we upload/download files over internet. SSD and/or HDD units are inserted Network Attached Storage Servers so that is how it works. It is ideal for content management systems, web serving, and big data analytics.
File Storage - Is different than block storage, while under the hood it depends on block based storage units, it is connected to internet so that we upload/download files over internet. SSD and/or HDD units are inserted Network Attached Storage Servers so that is how it works. It is ideal for content management systems, web serving, and big data analytics.
Object Storage - S3 is unlike the others mentioned above. With the help of REST API or aws cli tool we can download or upload files easily. There is no format restrictions we can upload file of any kind.
Let's create our own EBS unit and use it.
We can use EBS for other purposes as well, we can create AMI image snapshot and based on that create new EC2 instances easily.
Consider that since the EBS snapshots are exact copy of the volume itself, this kind of mistakes might occur. If we create our EC2 instance based on the user-data I have provided to you and then create AMI from it. Previous EC2 instance's IP address will be shown in the index.html file.
Let's create EFS storage unit and connect it to our EC2 instance
- First need to create EC2 instance, click to the volumes section.
- Since this unit has no file system whatsoever our OS won't able to mount it, so we need to make file system by mkfs command as below.
We can use EBS for other purposes as well, we can create AMI image snapshot and based on that create new EC2 instances easily.
- Click to create image button.
- Name it and finish the operation. You will be able to see your AMI created here
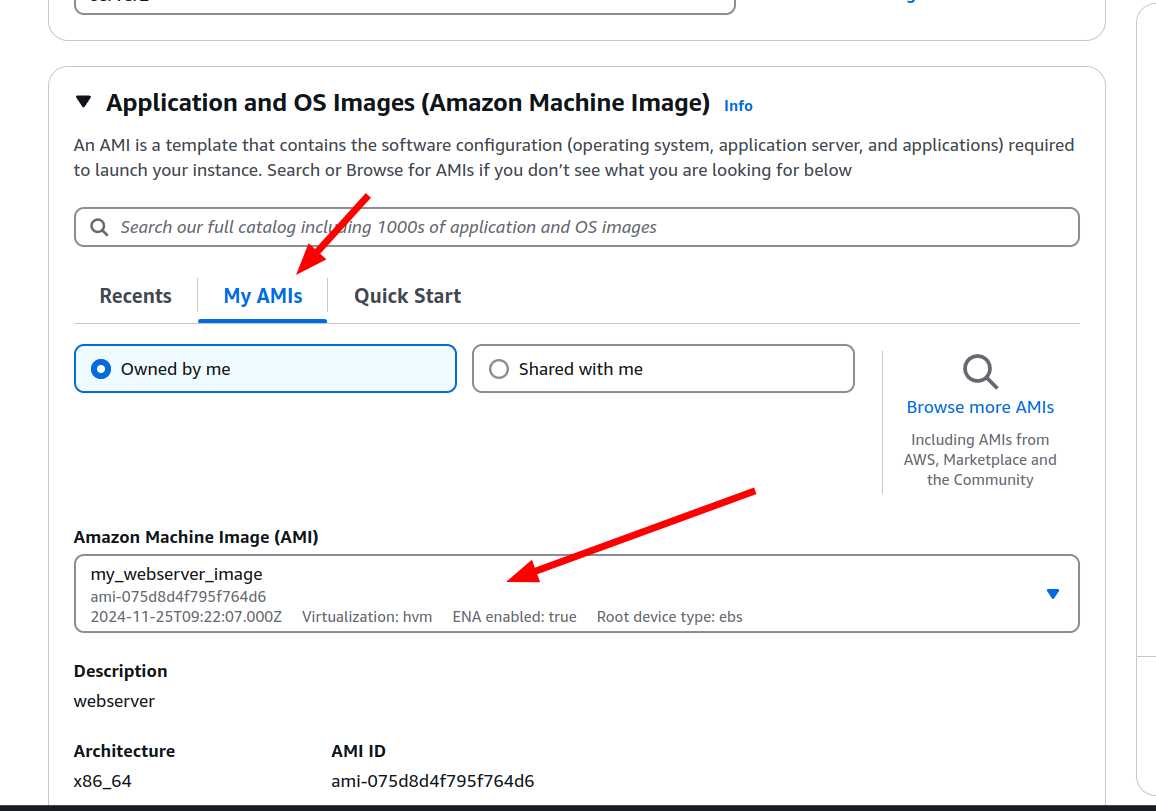
- All the custom AMI's located in My AMI's section in the EC2 instance creation phase.

Consider that since the EBS snapshots are exact copy of the volume itself, this kind of mistakes might occur. If we create our EC2 instance based on the user-data I have provided to you and then create AMI from it. Previous EC2 instance's IP address will be shown in the index.html file.
Let's create EFS storage unit and connect it to our EC2 instance
- Type EFS to the search bar and click to the icon as shown below
- Okay, make sure that you have already created the directory named "efs" as used in the command. When you navigate to that directory and create file there and connect to the same EFS instance using another EC2 instance you will see the files there too. This allows us to share files across different machines.




















Comments
Post a Comment